Passive2:PH case: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
SebSta (Diskussion | Beiträge) Keine Bearbeitungszusammenfassung |
SebSta (Diskussion | Beiträge) |
||
| (14 dazwischenliegende Versionen von 2 Benutzern werden nicht angezeigt) | |||
| Zeile 1: | Zeile 1: | ||
== General == | == General == | ||
=== Parameters === | === Parameters === | ||
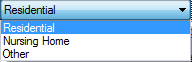
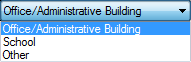
[[Bild:Passive-phcasegeneral.png|right|General]]In this section | [[Bild:Passive-phcasegeneral.png|right|General]]In this section the building category is chosen [[Bild:Passive-phcase_residentscope.png]]<br> and the occupancy type is chosen depending on which category is appropriate for the simulated building. There are different options, depending if the building is residential or not.<br> | ||
<div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_residental_scope.png|Residential]]</div> | <div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_residental_scope.png|Residential]]</div> | ||
<div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_nonresidental_scope.png|Non-residential]]</div><br><br><br> | <div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_nonresidental_scope.png|Non-residential]]</div><br><br><br> | ||
This choice | This choice influences the internal loads/heat gains.<br><br> | ||
The indoor temperature defines the mean indoor temperature during the heating period. The tooltip recommends 20°C (68°F) for residential buildings | The indoor temperature defines the mean indoor temperature during the heating period. The tooltip recommends 20°C (68°F) for residential buildings. For non-residential buildings, the calculation method is described in EN 13790.<br><br> | ||
The internal can either be calculated depending on the equipment or a predefined value can be used.<br><br> | The internal heat gains can either be calculated depending on the equipment or a predefined default value can be used.<br><br> | ||
There are two options for the occupancy setting: design and verification. The verification setting determines occupancy by the treated floor area and uses a predefined default value for internal gains. The design setting uses the occupant quantity from inner loads, as well as a calculated value for internal heat gains. Design is the default setting for non-residential buildings and cannot be changed. | |||
<br><br> | |||
The number of units represents the amount of dwellings in the building. | The number of units represents the amount of dwellings in the building. | ||
=== Zones === | === Zones === | ||
Additional zones can be implemented here, to calculate different | Additional zones can be implemented here, to calculate different zones at the same time. They can also be named here. | ||
== Additional data == | == Additional data == | ||
=== Required data === | === Required data === | ||
[[Bild:Passive-phcase additionaldata.png|right|Additional data]] | [[Bild:Passive-phcase additionaldata.png|right|Additional data]] | ||
The first two values describe the lower limit of indoor temperature achieved by ventilation and the maximum indoor temperature during summer.<br><br> | The first two values describe the lower limit of indoor temperature achieved by ventilation and the maximum indoor temperature during summer.<br><br> | ||
The design air volume flow rate is defined by the maximum of either<br> | |||
For the building wind exposure, WUFI has | * Supply air per person * occupancy | ||
* Extract air requirements per room | |||
* Volumetric requirement (0.3 air changes per hour), or shown as (0.3 x 1.3 x ventilation volume x (1/60)) | |||
<br> | |||
To account for the air tightness of the building, a measured value from the blower door test (ACH 50 test) and the net air volume are required.<br><br> | |||
Another important parameter for the calculation of the sensible cooling demand is the Max. Humidity Ratio. If the Humidity Ratio of the outer air (defined by the ambient temperature and the dew point) for a specific month is greater than this value, it is usually necessary to dehumidify the air.<br> | |||
To estimate a realistic value, WUFI contains a calculator which can be found by clicking on "..." in this window. This tool can calculate the humidity ratio for given air temperature and dew point.<br><br> | |||
For the building wind exposure, WUFI has predefined values, which can be chosen from the "Building wind exposure" scope. You can also use the "User defined" tab and input values yourself.<br> | |||
[[Bild:Passive-phcase_adddata_scope_wind.png|Scope wind exposure]] | [[Bild:Passive-phcase_adddata_scope_wind.png|Scope wind exposure]] | ||
=== Optional Data === | === Optional Data === | ||
These values can be | These values can be entered if available but are not necessary. If not defined, WUFI does calculate them. | ||
== Foundation interface == | == Foundation interface == | ||
[[Bild:Passive-phcase_foundint.png|right|Foundation interface]] | [[Bild:Passive-phcase_foundint.png|right|Foundation interface]] | ||
WUFI® calculates the ground temperature depending on the type of foundation (Reference:EN ISO 13370). There are four different types are available. You also have the option to let WUFI detect the given type by itself or input your own ground temperature measurement. This measurement must be entered in the climate file and will be shown in the fourth row of the [[Passive2:Dialog_Climate#Climate|Climate tab]].<br> | |||
[[Bild:Passive-phcase_foundint_scope.png|Foundation scope]] | |||
=== Parameters === | |||
Depending on the type of foundation, different values are needed for WUFI. You have the option to either specify them yourself or let WUFI detect them automatically. | |||
<div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_foundint_unheatedbasement.png|thumb|Unheated basement]]</div> | |||
<div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_foundint_slabongrade.png|thumb|Slab on grade]]</div><br style="clear:both" /> | |||
<div class="tleft" style="clear:none">[[Bild:Passive-phcase_foundint_suspendedfloor.png|thumb|Suspended floor]]</div> | |||
Aktuelle Version vom 10. Juni 2014, 09:27 Uhr
General
Parameters
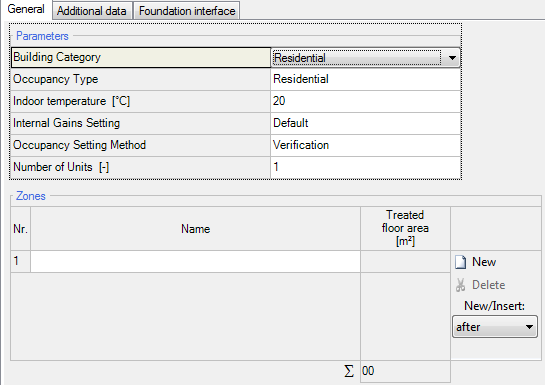
In this section the building category is chosen 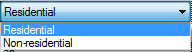
and the occupancy type is chosen depending on which category is appropriate for the simulated building. There are different options, depending if the building is residential or not.
This choice influences the internal loads/heat gains.
The indoor temperature defines the mean indoor temperature during the heating period. The tooltip recommends 20°C (68°F) for residential buildings. For non-residential buildings, the calculation method is described in EN 13790.
The internal heat gains can either be calculated depending on the equipment or a predefined default value can be used.
There are two options for the occupancy setting: design and verification. The verification setting determines occupancy by the treated floor area and uses a predefined default value for internal gains. The design setting uses the occupant quantity from inner loads, as well as a calculated value for internal heat gains. Design is the default setting for non-residential buildings and cannot be changed.
The number of units represents the amount of dwellings in the building.
Zones
Additional zones can be implemented here, to calculate different zones at the same time. They can also be named here.
Additional data
Required data
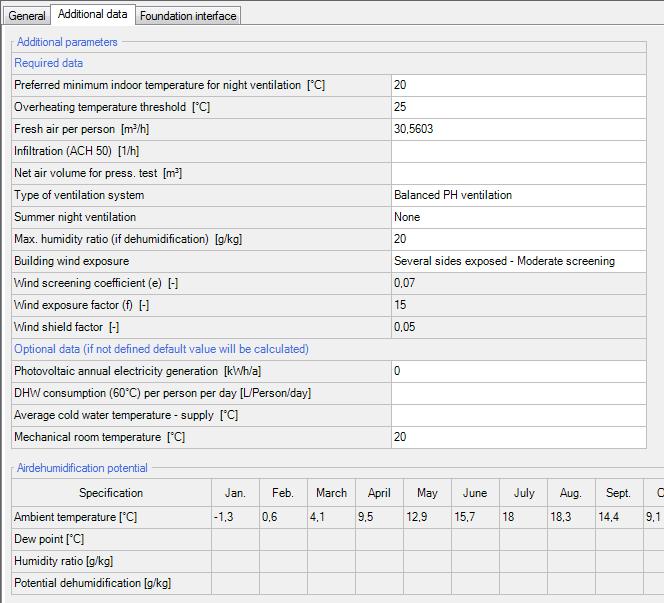
The first two values describe the lower limit of indoor temperature achieved by ventilation and the maximum indoor temperature during summer.
The design air volume flow rate is defined by the maximum of either
- Supply air per person * occupancy
- Extract air requirements per room
- Volumetric requirement (0.3 air changes per hour), or shown as (0.3 x 1.3 x ventilation volume x (1/60))
To account for the air tightness of the building, a measured value from the blower door test (ACH 50 test) and the net air volume are required.
Another important parameter for the calculation of the sensible cooling demand is the Max. Humidity Ratio. If the Humidity Ratio of the outer air (defined by the ambient temperature and the dew point) for a specific month is greater than this value, it is usually necessary to dehumidify the air.
To estimate a realistic value, WUFI contains a calculator which can be found by clicking on "..." in this window. This tool can calculate the humidity ratio for given air temperature and dew point.
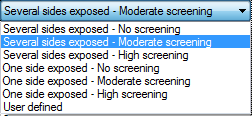
For the building wind exposure, WUFI has predefined values, which can be chosen from the "Building wind exposure" scope. You can also use the "User defined" tab and input values yourself.
Optional Data
These values can be entered if available but are not necessary. If not defined, WUFI does calculate them.
Foundation interface
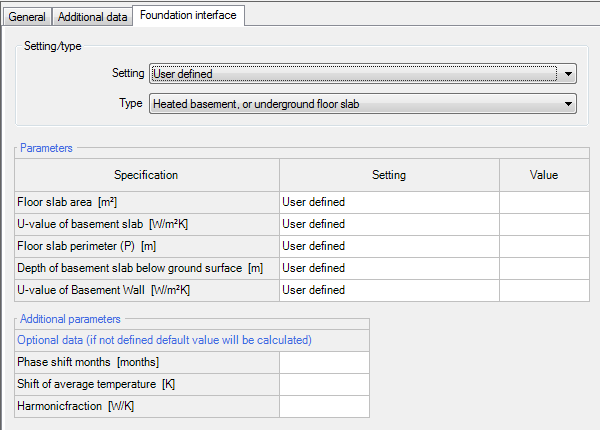
WUFI® calculates the ground temperature depending on the type of foundation (Reference:EN ISO 13370). There are four different types are available. You also have the option to let WUFI detect the given type by itself or input your own ground temperature measurement. This measurement must be entered in the climate file and will be shown in the fourth row of the Climate tab.
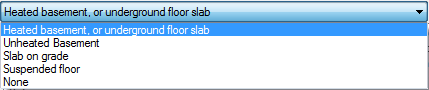
Parameters
Depending on the type of foundation, different values are needed for WUFI. You have the option to either specify them yourself or let WUFI detect them automatically.